There are estimated to be 1.9 million Australians living with diabetes and 300 Australians develop diabetes every day. So how can a podiatrist help?
Diabetes is a condition in which there is too much glucose in the blood. The body can not make insulin/enough insulin or not effectively use the insulin it makes. There are three main types of diabetes; Type 1, Type 2 and Gestational diabetes. Overtime, the high blood glucose levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, resulting in further health complications such as heart, kidney, eye and foot damage.
What role does podiatry play in diabetes?
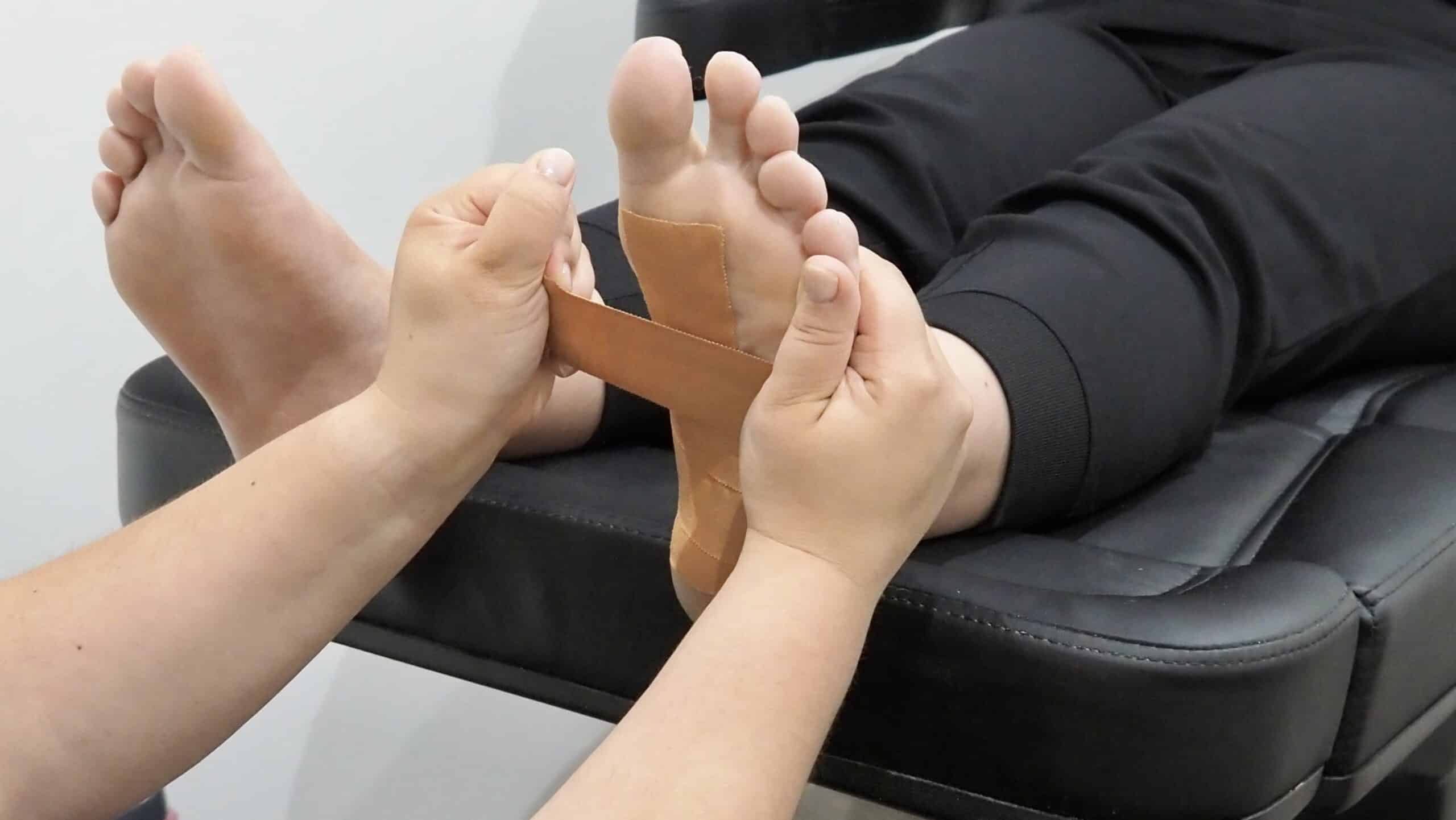
Screening for potential foot related complications
- Podiatrists are able to use a variety of tools to assess and screen for complications. Depending on the risk factors a patient has will determine the frequency of assessment performed in one year.
Neurovascular Assessment
- Vascular assessments are performed to assess circulation to the feet. Our podiatrists will identify nail growth, hair growth, skin colour, temperature and pulses to the feet. In addition, a doppler ultrasound can be performed to examine the waveform of each pedal pulse and compare with previous readings. From here, further imaging might be required if reduced arterial flow is suspected.
- Neurological assessments are performed to assess nerve function within the feet. A podiatrist will perform a superficial testing by applying a 10g monofilament to specific sites on the foot, this will indicate if there is a loss of protection sensation. Deep nerve sensation is also assessed by using a 128Hz tuning fork which will determine if a patient is at great risk of falls and injury.
Dermatological assessment
- Performing general nail and skin care regularly is important to identify any issues such as ingrown toenails, corn or callus, blisters or open wounds. If any of these issues are present there is an increased risk of skin break down, infection and ulceration.
Biomechanical assessment
- Conditions such as flat arched feet, high arched feet, reduced range of motion, bony prominences, toe deformities or bunions all have the potential to cause increased pressure to particular areas of the feet. Increased pressure could lead to callus formation, which if left untreated the skin beneath can lose its elasticity and moisture and break down underneath, forming ulceration.
Footwear
- Education surrounding footwear is vital to ensure the feet are well supported, stable and protected.
If you have any questions about podiatry or need your annual diabetic foot assessment, feel free to give us a call on 8468 2411 or book in here.